Desert Biome
Climate/Water Type
Desert Biomes have very minimal percipitation, a very dry and warm climate, with hot days and cold nights. They have less than 25 cm of rain and their temperatures range from around 15-30°C.
Location (Latitude, Continets)
Desert biomes are found across the globe, They are typically located between 15 and 30 degrees latitude, both north and south of the equator. Major desert biomes can be found in North and South America, North Africa, Central Austriia
3 Animals and Their Adaptations
- Camels have humps to store fat for energy and can close their nostrils to keep out sand.
- Fennec foxes have large ears to dissipate heat, thick fur for insulation, and are nocturnal to avoid daytime heat
- Sidewinder snakes move sideways to avoid sinking in sand and are nocturnal to avoid daytime heat.
2 Plants and Their Adaptations
- Saguaro cacti have shallow roots to absorb rainfall quickly, expandable stems to store water, and waxy skin to reduce evaporation.
- Aloe vera stores water in its gel-filled leaves, has shallow roots for quick water absorption, and can go dormant during droughts.
5 Important Facts
- Currently deserts cover around 20% of the world's land, but they are growing, due to desertification
- Because the desert is so dry, the wind will grind pebbles and sand into dust. Occasionally a big wind storm will gather up this dust into a huge storm.
- Only certain types of plants can survive the harsh environment of the desert, because of this the desert has very sparse vegetation and plants.
- Desert habitats have been harmed by road building and oil drilling that pollute and disrupt the desert habitat
- Many oils and minerals are being taken out of the desert that cannot be replaced, causing more damage to the environment.
5 Questions to distinguish the desert biome from other biomes
- Does this biome get minimal percipitation?
- Does this biome have a hot and dry climate?
- Does this biome have sparse vegetation and plants?
- Does this biome have hot days and cold nights?
- Does this biome have many nocturnal animals?
Climatograph of the desert
Tundra Biome
Climate/Water Type
Tundra Biomes have very minimal percipitation, a very cold and warm climate, with long winters and short summers. They have around 10 inches of percipitation per year and their temperatures range from around 4-10°C.
Location (Latitude, Continets)
Tundra biomes are found near the north pole, They are typically located between 60 and 75 degrees latitude, north of the equator. Major desert biomes can be found in North and North America, northern Europe, and northern Asia.
3 Animals and Their Adaptations
- Caribou migrate to warmer areas during the winter to avoid the extreme cold.
- Artic Fox have loarger bodies and smaller limbs to minimize heat loss, while their fur helps them blend in with the snowy landscape.
- Polar bears hibernate in the winter and have two layer of fur for extra warmth.
2 Plants and Their Adaptations
- Arctic Moss stores nutrients so new leaves can be made quickly next spring when it is not growing.
- Arctic Willow has a shallow root system to avoid permafrost and long fuzzy hairs to protect it from the cold weather.
5 Important Facts
- Tundra's have permafrost, which is a thick layer of soil that remains frozen throughout the year.
- The tundra is baren, it has few nutrients to support plant and animal life. It has a short growing season and a slow rate of decay.
- The tundra has two distinct seasons: a long winter and a short summer, it also has long nights in the winter and long days in the summer.
- The tundra is a very fragile biome that is shrinking as the permafrost melts, due to global warming.
- Many plants and animals have to resort to extreme measures to keep warm, for example plants grow in tight groups and animals have small ears and tails.
5 Questions to distinguish the Tundra biome from other biomes
- Does this biome get minimal percipitation?
- Does this biome have a cold and dry climate?
- Does this biome have sparse vegetation and plants?
- Does this biome have long winters and short summers?
- Does this biome have permafrost?
Climatograph of the Tundra

Savanna Biome
Climate/Water Type
Savanna Biomes have a wet and dry climate, with a long dry season and a short wet season. They have around 20-50 inches of rain per year and their temperatures range from around 20-30°C.
Location (Latitude, Continets)
Savanna biomes are found near the equator, They are typically located between 5 and 15 degrees latitude, both north and south of the equator. Major savanna biomes can be found in Africa, South America, and Australia.
3 Animals and Their Adaptations
- African Elephants have long trunks that allow them to reach high branches for food and to spray water on their bodies to cool down in the hot savanna climate.
- Egyptian mongooses claws have adapted to digging allowing them to dig bugs out of the ground, so they can avoid predation and heat
- Zebra have stripes that help them blend in with the tall grasses of the savanna, and they have long legs to run away from predators.
2 Plants and Their Adaptations
- In the wet months Baobab store water in its thick, corky, fire-resistant trunk for the nine dry months ahead.
- Jarrah tree's have a large swelling underground that can store carbohydrates, and can make it possible for a young jarrah to grow back after a fire.
5 Important Facts
- Many of the animals in the savanna have long legs which helps them when migrating long distances.
- Overgrazing and farming has destroyed much of the savanna. When overgrazing occurs, the grasses don't grow back and the savanna can turn into desert.
- Fires are an important part of the savanna. During the dry season fires clear out old dead grass and make way for new growth.
- Many animals of the savanna are endangered due to overhunting and loss of habitat.
- The savanna is a type of grasslands biome. The savanna is sometimes called the tropical grasslands.
5 Questions to distinguish the Savanna biome from other biomes
- Does this biome have rainy and dry seasons?
- Does this biome have a warm climate?
- Does this biome have large heards of animals?
- Does this biome have scattered trees and shrubs?
- Is this biome located in middle latitudes?
Climatograph of the Savanna
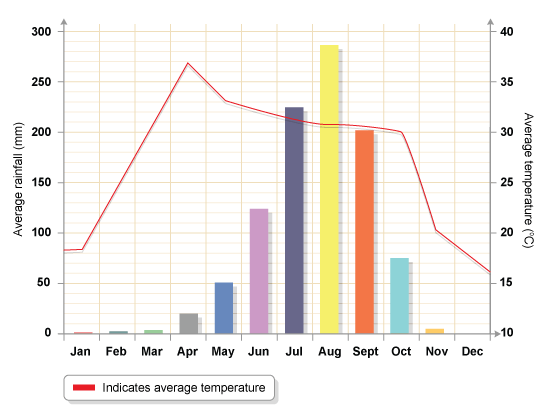
Grassland Biome
Climate/Water Type
Grassland Biomes have a moderate percipitation, with a 4 seasons. They have around 25-50 inches of rain per year and their temperatures range from around 20-30°C.
Location (Latitude, Continets)
Grassland biomes are found mainly in the northern hemisphere, They are typically located between 30 and 60 degrees latitude, both north and south of the equator. Major grassland biomes can be found in North and South America, Europe, and Asia.
3 Animals and Their Adaptations
- Prairie dogs need very little water; the water from the plants they eat provide enough hydration, and their sharp teeth are perfect for easily clipping grasses.
- Bisons have broad, flat-topped teeth and digestive systems especially adapted to feed on grasses.
- Coyote's thick fur helps to keep it warm throughout the winter. Its color blends in with the environment, providing the coyote with excellent camouflage.
2 Plants and Their Adaptations
- Buffalo grass has adapted to grassland fires and sometimes grows better after a fire, the actual growing parts of buffalo grass are protected from fire by soil.
- Pampas Grass has a deep root system that digs down and finds water so it can survive in the driest areas.
5 Important Facts
- The grassland biome plays an important role in human farming and food, they are used to grow staple crops such as wheat and corn, also they are good for grazing livestock such as cattle.
- Unfortunately, human farming and development has caused the grassland biome to steadily shrink.
- Scientists believe that occasional fires help to rid the land of old grasses and allow for new grasses to grow, bringing new life to the area.
- Grasslands are generally located between deserts and forests.
- Grasslands are wide expanses of land filled with low growing plants such as grasses and wildflowers.
5 Questions to distinguish the Grassland biome from other biomes
- Does this biome have 4 seasons?
- Does this biome have moderate percipitation?
- Does this biome have many grazing animals?
- Is this biome mainly found in the northern hemisphere?
- Is this biome dominated by grasses?
Climatograph of the Grassland

Taiga Biome
Climate/Water Type
Taiga Biomes have a moderate to little percipitation, with a short growing season. They have around 12-30 inches of rain per year and their temperatures range from around -20-10°C.
Location (Latitude, Continets)
Taiga biomes are found mainly in the northern hemisphere, They are typically located between 50 and 70 degrees latitude, north of the equator. Major taiga biomes can be found in North America, Europe, and Asia.
3 Animals and Their Adaptations
- Moose have long legs to wade through deep snow and can eat twigs and bark when food is scarce.
- Snowshoe hares have large feet that act like snowshoes, allowing them to move quickly over the snow.
- Siberian tigers have thick fur to keep them warm in the cold, and they have a thick layer of fat to help them survive when food is scarce.
2 Plants and Their Adaptations
- Balsam Fir has a waxy coating on its needles to prevent water loss and can grow in the shade of other trees.
- Black Spruce has a shallow root system that can absorb nutrients from the soil and can grow in the acidic soil of the taiga.
5 Important Facts
- The taiga is the largest biome in the world, covering large parts of North America, Europe, and Asia.
- The taiga is a cold forest biome that is dominated by coniferous trees like pine, spruce, and fir.
- The taiga has a short growing season and long, cold winters. The trees in the taiga are adapted to the cold and have needle-like leaves that help them conserve water.
- The taiga is home to a variety of animals, including moose, bears, wolves, and lynx.
- The taiga is an important habitat for many migratory birds, including warblers, thrushes, and sparrows.
5 Questions to distinguish the Taiga biome from other biomes
- Does this biome have evergreen trees?
- Does this biome have cold weather?
- Is this biome dry?
- Does this biome have a thin layer of soil?
- Does this biome have a short growing season?
Climatograph of the Taiga

Temperate Forest Biome
Climate/Water Type
Temperate Forest Biomes have lots of percipitation, with 4 distinct seasons. They have around 30-60 inches of rain per year and their temperatures range from around -30-30°C.
Location (Latitude, Continets)
Temperate Forest biomes are found around halfway between the equator and the poles, They are typically located between 30 and 60 degrees latitude, both north and south of the equator. Major temperate forest biomes can be found in North and South America, Europe, Australia, and Asia.
3 Animals and Their Adaptations
- White-tailed deer have a reddish-brown coat in the summer and a grayish-brown coat in the winter to help them blend in with their surroundings.
- Red foxes have thick fur to keep them warm in the winter and can run up to 30 miles per hour to catch prey.
- Black bears hibernate in the winter to conserve energy and have a keen sense of smell to find food.
2 Plants and Their Adaptations
- Sugar Maple has a shallow root system that can absorb nutrients from the soil and can grow in the acidic soil of the temperate forest.
- Eastern Hemlock has a waxy coating on its needles to prevent water loss and can grow in the shade of other trees.
5 Important Facts
- The temperate forest is the most common biome in the world, covering large parts of North America, Europe, and Asia.
- The temperate forest is a forest biome that is dominated by deciduous trees like oak, maple, and beech.
- The temperate forest has a long growing season and mild winters. The trees in the temperate forest are adapted to the cold and have broad leaves that help them capture sunlight.
- The temperate forest is home to a variety of animals, including deer, bears, wolves, and squirrels.
- The temperate forest is an important habitat for many migratory birds, including warblers, thrushes, and sparrows.
5 Questions to distinguish the Temperate Forest biome from other biomes
- Does this biome have temperate temperature?
- Does this biome have four distinct seasons?
- Does this biome have trees that lose teir leaves?
- Does this biome have a ferile soil?
- Does this biome have lots of rain?
Climatograph of the Temperate Forest
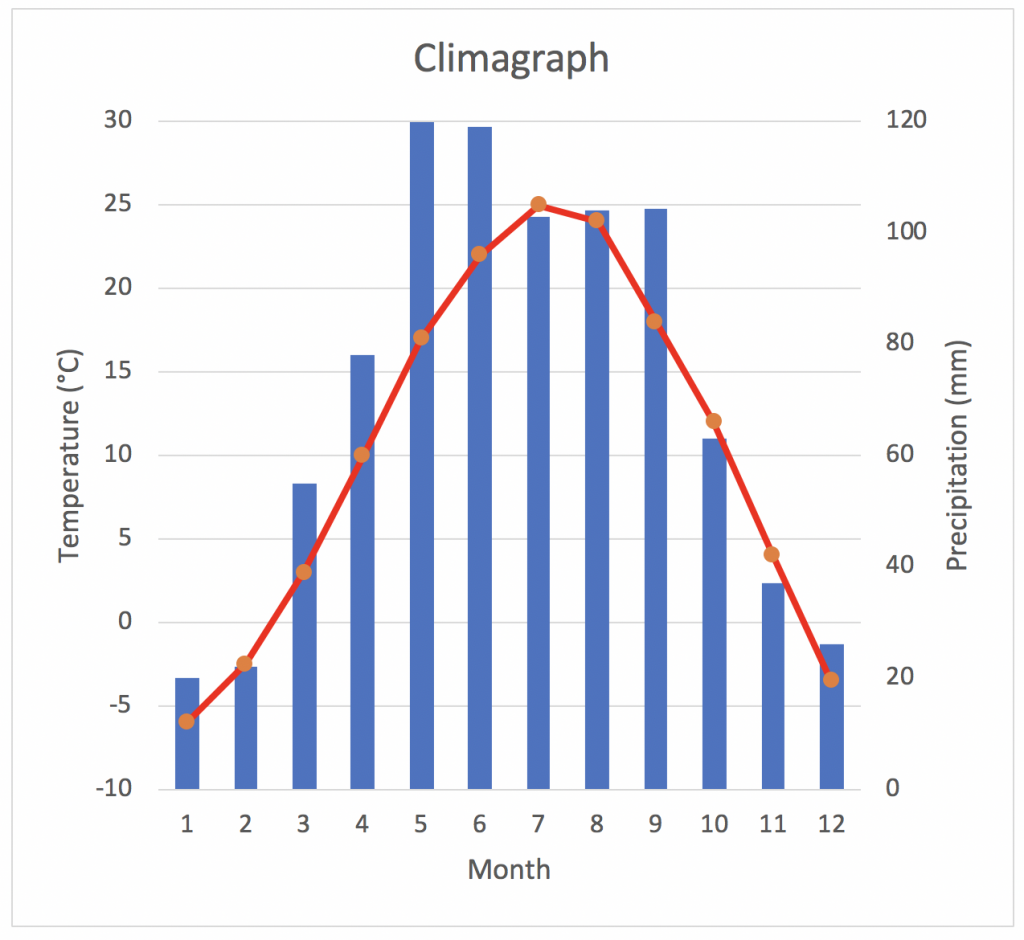
Tropical Rainforest Biome
Climate/Water Type
Tropical Rainforest Biomes have tons of percipitation, with a hot and wet climate. They have around 60-200 inches of rain per year and their temperatures range from around 20-30°C.
Location (Latitude, Continets)
Tropical Rainforest biomes are found near the equator, They are typically located between 0 and 10 degrees latitude, both north and south of the equator. Major tropical rainforest biomes can be found in South America, Africa, and Asia.
3 Animals and Their Adaptations
- Toucans have large, colorful beaks that help them reach fruit high in the trees and are used to attract mates.
- Sloths have long claws that help them hang from trees and move slowly to conserve energy.
- Jaguars have sharp teeth and claws to catch prey and are excellent swimmers.
2 Plants and Their Adaptations
- Orchids have bright colors and strong scents to attract pollinators and can grow on other plants to reach sunlight.
- Bromeliads have leaves that form a cup to collect water and can grow on other plants to reach sunlight.
5 Important Facts
- The tropical rainforest is the most diverse biome in the world, with millions of species of plants and animals.
- The tropical rainforest is a forest biome that is dominated by broadleaf trees like mahogany, teak, and rosewood.
- The tropical rainforest has a hot and wet climate with a long growing season. The trees in the tropical rainforest are adapted to the heat and have broad leaves that help them capture sunlight.
- The tropical rainforest is home to a variety of animals, including monkeys, parrots, and snakes.
- Unfortunately, human development is killing off much of the world's rainforest.
5 Questions to distinguish the Tropical Rainforest biome from other biomes
- Does this biome have tons of rain?
- Does this biome have hot weather?
- Is this biome wet?
- Does this biome have a lots of biodiversity?
- Is this biome being destroyed by human development?
Climatograph of the Tropical Rainforest
